Opportunity
Problem
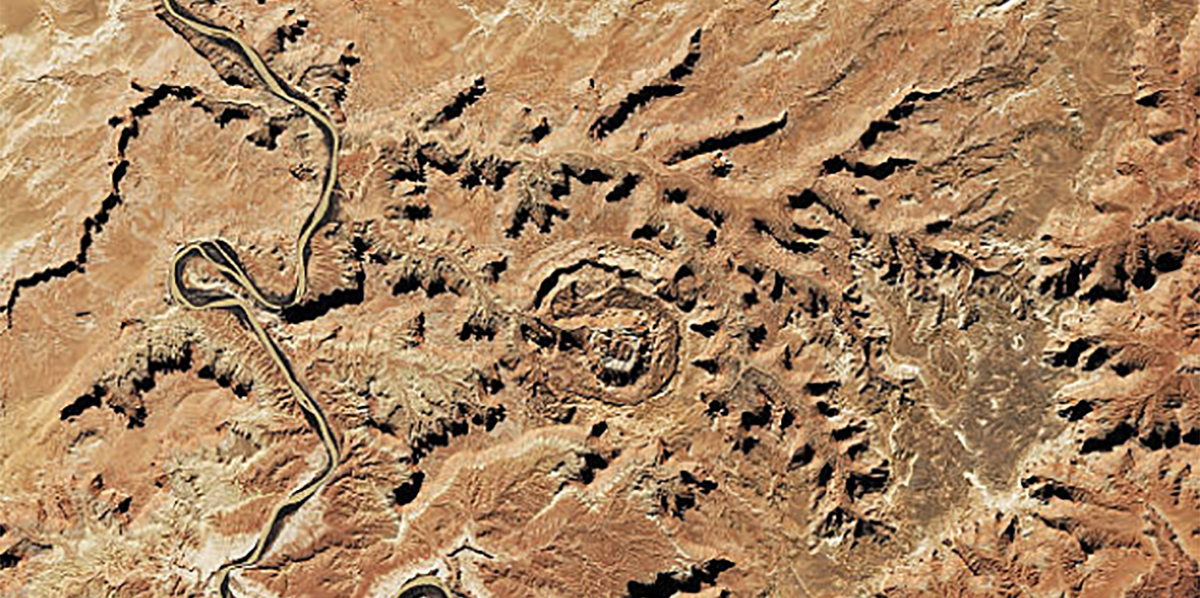
What process caused this formation?
Here are a few tips to get the most out of our sample business plans and build the plan your business needs to succeed.
Find a plan from a similar industry to your business, but don’t worry about finding an exact match. In fact, you won’t find an exact match for your business. That’s because every business is as unique as its owners and managers. Every business has a different location, different team, and different marketing tactics that will work for them. Instead of looking for an exact match, look for a business plan that’s for a business that operates similarly to how your business will work. For example, a business plan for a steak restaurant will actually be useful for someone starting a vegetarian restaurant because the general concepts for planning and starting a restaurant are the same regardless of what type of food you serve.
Use the sample plans for inspiration and ideas. Staring at a blank page can be the worst part of writing a business plan. In fact, that’s probably the reason that’s preventing you from getting started right now. Instead, take advantage of our sample plans to avoid writer’s block. Feel free to copy words, phrasing, and the general structure of a plan to start your own. Also, as you read through several plans, you might find ideas for your business that you hadn’t considered. Use our plans for inspiration and ideas, borrow phrasing when it makes sense, and just get going!
Write a business plan that’s right for your business. As tempting as it is, don’t just cut and paste from a sample plan. Any banker or investor will be able to tell from miles away that you copied someone else’s plan. Not only will you be less likely to get funding if you copy a business plan, you’ll be greatly reducing your chances of success because you didn’t write a plan that’s right for your specific business, its specific location, target market, and your unique product or service. Thinking through how you are going to launch your business is a critical step in starting a business that you shouldn’t let go.
The value of business planning is in the process, not the final document. By creating your own business plan, you are going to have to think about how you are going to build your own business. What marketing tactics are you going to use? What kind of management team do you need to be successful? How is your business going to set itself apart from the competition?
The process of writing a business plan guides you through answering these questions so that you end up with a strategy that works for your business. You will also end up with a plan that you can share with business partners, investors, and friends and family. Sharing your vision and your strategy is the best way to get everyone on the same page and pushing forward to build a successful business.
Use your plan as a management tool and build a better business. When you’re done with your plan and your business is up and running, your plan shouldn’t just end up in a drawer. That would be a huge waste of all the time and effort you put into your strategy, budgets, and forecast. Instead, using your plan as a tool to grow your business can be one of the most powerful things you can do to grow your business. In fact, businesses that use their plan as a management tool to help run their business grow 30% faster than those businesses that don’t.
To use your business plan to grow 30% faster than the competition, you need to track your actual results – the sales that you get and the expenses that you incur – against the goals that you set out for yourself in your plan. If things aren’t going according to plan, perhaps you need to adjust your budgets or your sales forecast. If things are going well, your plan will help you think about how you can re-invest in your business. Either way, tracking your progress compared to your plan is one of the most powerful things you can do to grow your business.
Need more? Check out our philosophy on lean planning and download a free business plan template to get your business started.
LivePlan logo
LivePlan makes business planning easy
GET THE MOST OUT OF SAMPLE PLANS
Bplans has over 500 sample plans to learn from. Before reading the plan, hear what the business planning experts have to say about getting the most out of business sample plans. Learn More »
LOOKING FOR SOMETHING DIFFERENT?
If our sample plan isn’t exactly what you are looking for, explore our free business plan template. Or, create your own custom business
//////////////////////////////////////////
Presentations – Networking – Business Plan
http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5757-4724
ArgosVu_VRARA_PRESENTATION_10_25_2018_005.pptx
ArgosVu_VRARA_PRESENTATION_10_25_2018_005.pdf
Speaker Info
VRARA LA Presents: The Path to FundingThurs, Oct 256:30 – 9:30pm
Keynote: Morgan Mercer, Vantage Point
Morgan Mercer is the founder of the VR-based enterprise training company, Vantage Point. Vantage Point’s suite of immersive training tools is initially aiming at tackling anti-sexual harassment training with plans of expansion into unconscious bias and managerial training. Mercer was recently regarded as one of the Top 10 Female Tech Innovators [in history] by TechRadar and has been featured in 3+ dozen publications including WIRED, The Guardian, and NPR.
—
Panel Moderator: Jason McDowall, The AR Show
Jason is a serial entrepreneur – first in mobile, later in AI-assisted CRM. He also spent several years at Salesforce.com. Today he’s a VP at a company addressing one of the most fundamental challenges of see-through AR smartglasses: the underlying visual engine. Jason is also an active angel investor and the host of the premier podcast focused on augmented reality called The AR Show.
—–
Panelist: Martina Welkhoff, The WXR Fund
Martina Welkhoff is a serial entrepreneur and investor with growth and acquisition experience. She’s a Founding Partner at the WXR Fund, a venture fund focused on women-led AR/VR companies, and a Venture Partner at Jump Canon, a San Francisco fund focused on underrepresented founders in emerging tech.
She is a board member of Seattle Angel and advisor to the Center for Leadership and Strategic Thinking at the University of Washington, and for over five years was the President of Seattle Women in Tech. Martina is a World Economic Forum Global Shaper, a member of the Young Entrepreneurs Council, and an alumna of the Schusterman Foundation REALITY program.
—-
Panelists: Marco DeMiroz, The Venture Reality Fund
Marco is the co-founder and a general partner of The Venture Reality Fund, where he oversees the company’s investments in early-stage augmented/mixed/virtual reality, as well as Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Blockchain startups.
He has extensive experience in executive roles with leading technology companies and in global investments. Marco has focused on strategic investments across media, entertainment, lifestyle, sports and technology with firms most recently with Evolution Media Capital, where he led its investment in JauntVR. In addition to his role at The VR Fund, Marco actively advises numerous media and technology companies in the VR and AR sectors and has been collaborating in the formation of the Women in XR (“WXR”) Fund.
—-
Panelist: Lara Jeremko, Beyond Ventures
Lara Jeremko is Founder & Managing Partner of Beyond Ventures, a venture capital firm and content production studio focused on responsible innovation. She is an early stage angel investor and producer of JOBSOLETE, a documentary film exploring automation and the future of work. Most recently, Lara was Prize Lead for the XR Education Prize Challenge funded by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation. Lara has served as a Strategic Advisor to prominent venture capital funds including Foundry Group Next, Techstars, and Pivotal Ventures.
—-
Panelist: Teppei Tsutsui, GFR Fund
As an active investor for the past decade, Teppei Tsutsui is the CEO and Managing Director of GFR Fund. Having led several key investments and acquisitions in Tokyo, including GREE’s acquisitions of OpenFeint and Funzio, Teppei is currently leading GFR Fund in San Francisco. Prior to working for GREE, Teppei was key to advising M&A strategy at Morgan Stanley, where his strength in the Asian market and as an investor grew. He also worked in Japan in business development at Mitsubishi Corporation.
—–
Panelist: Kevin Zhang, Upfront Ventures
Kevin joined Upfront Ventures in 2012. Most recently, Kevin was at Boston Consulting Group, where he advised on strategy and operations for technology, healthcare, and industrial goods clients in the US and Asia and conducted due diligence for private equity investors. Previously, Kevin worked at Verisk Health, a healthcare IT startup in Boston, focusing on project management, product development, and consulting for strategic accounts.
Parking
nfernandez@thevrara.com

Perfecting the 3 Minute Startup Pitch
Problem
Philosophical Materialism
As we experience our education, the message we accept is that Science provides us with a world view that is rational, verifiable and empirically objective.
Issac Newton Newton’s Apple, falling from the tree… fails to take into account how the apple got up there in the first place.
We are indoctrinated into a world view that is inherently entropic, and bizarrely unable to present any workable explanation of the most fundamental element of measure, our own perception and consciousness.
——————————————————————————————————
Always start with the problem.
If you do anything at the beginning of your pitch other than talk about the problem, there’s a high chance your audience will have to work hard to adjust to what you’re talking about. Your audience is not ready to begin to digest the meat of your presentation from the first sentence of your pitch.
Do not jump into your product or service right away. This is especially true for an audience that may be unfamiliar with the problem space you’re tackling. By stating the problem first you prepare your audience with some background beforehand.
That background can go into the industry you are tackling or the landscape that you are working in. For an unfamiliar topic, you can provide some of the ‘before-we-start need-to-knows’ for the audience. Once the audience is primed, only then can you begin to talk about your solution.
Solution
Your solution should, in general, directly follow the problem. You want to make sure that you get across exactly what it is that you are doing and what your unique quality or main selling point is.
Don’t be vague. At the end of your pitch, if all else fails, your audience should know exactly what it is you do.
It is only after you explain whatyour solution is that your audience can start to absorb why your solution is, say, better/faster/cheaper than your competition. After this point in the pitch, your audience should be able to repeat back to you what it is you do with some certainty.
Once your audience understands what you’re doing and what problem you’re solving, you can move onto the the nitty-gritty details in the formula.
*The following can be reordered as you see fit.
Competition
Your industry probably has competitors. In some industries, you may have very many competitors, whereas in others, a few really big ones. Address the existing competitors head on. They are the elephant in the room. Put up the logos of competitors your audience most likely thinks your solution resembles. Talk directly about how or why your solution is better or different. And if you have deeply entrenched competitors, use this time to talk more about how you’ll break into your industry and take market share away from incumbents more so than what your unique product features are.
If you truly don’t have any competitors, or only have competitors that your audience is likely to have never heard of, mention something to the extent of what you’ve done to search or prove that an existing solution does not exist. Don’t leave the audience thinking you’re avoiding your competition.
And if you have big players in your space but they are not competing directly with you, you should still call them out and explain how your solution will fit in and live with these existing competitors in your market.
Market
Who is in your target demographic? How big is the market for your product? What is the specific market size of your product and how is it changing year over year? These are all good things to point out to give your audience a sense of scale for how large your business can grow.
But again, don’t be vague, especially when talking about your addressable market size. If you are creating a fitness app, you should not be taking the entire market for fitness and fitness related products as your addressable market size. If you are building a chatbot for buying clothes online, you should not say that the addressable market for your product is the entire clothing industry. Find your overarching market, then find subdomains within it until the market you decide on is a reasonable size that you could realistically see your startup taking a big slice out of.
And if you do have a big addressable market, do not use the “If we could only get .1% of this huge market we’ll be a $B dollar company” line. The market you are playing into has incumbents and status quo effects. If you do say you’re planning to take .1% of the market, you better have some great reasons to back up that claim.
Traction
Traction is likely the most crucial partof your entire pitch. Traction is all about validity. For those individuals in your audience that are well versed in your industry and what you are making, they can form their own opinions about the likelihood of success for your business. For everyone else in your audience, their opinions will be swayed by cold hard data.
If you say you’re planning on building X, talk about what you’ve already built, in what length of time. If you’ve launched a pilot or run demos, talk to how those went.
If you say that your target market will buy X, present the numbers: how many have already purchased, for how much, over what period of time?
If you haven’t sold anything or are more early stage, there are still plenty of other things you can mention. Talk about how many people put their name on your mailing list, downloaded your app, visited your website, registered, have come back week over week.
Anything you can show that emphasizes that you are the real deal and that real people want what you are offering should be laid out for your audience.
The traction you choose to highlight should be that which is most relevant to your business being a success. If you’ve received press you should mention that as well, but press alone is not a positive justification for your business model. The number of users, retention, customer satisfaction; those metrics that are most relevant to your business should be at the front and centre of your pitch when covering traction.
Team
You don’t need to go into the life story of each of your team members, but show that the skill-set of the people on your team matches the skill-set required to pull of the solution you are pitching. If you are pitching a software product and only have people with business experience on your team, maybe you don’t have the right team for the solution. Same thing goes for building a hardware product with no team members with engineering experience, or building a life sciences company with no one that has a bio-background. Your team and combined experience provides the legitimacy for whether you’re the right people to bring your solution to the world.
If there’s a mismatch between your team’s experience and your proposed solution, the only thing that can save you in that case is traction and what you’ve already built. Only in that case, because you’ve already built something that proves you can complete your solution regardless of your team’s expertise, your lack of experience becomes less of a red flag.
You should also mention any mentors you have at this point, so long as your audience knows of or is explained the role and/or importance of those mentors to your team.
Future
You’ve explained the problem. You’ve described your solution. You’ve explained how you’re better/faster/cheaper than the competition and pinpointed the size of your addressable market. You’ve talked about your team’s expertise and covered all of the traction you’ve had to date. Now that your audience is up to speed, it’s time to let them know what the next steps are. What it is that you’ll be doing, in both the near and more distant future, that your audience can cheer you on for.
In the near future, talk about any pilots you’re planning to run, Kickstarters you’re planning to launch or users you’re planning to onboard. Talk about partnerships you have in place, sales you will be closing, shipments you’ll be making or deployments you will be executing on.
Then, talk about what you plan for the company to achieve in the long run, whether that be a sales target or mission statement. End off on selling the dream. When all is said and done, your audience will be the ones choosing for themselves whether or not they want to climb aboard your rocketship of an idea.